

Full coverage car insurance is a term you usually come across when searching for an auto policy. But what does this form of coverage really mean?
Is it a type of car insurance policy that protects against every possible scenario? Or is it an add-on that allows you to access the highest level of protection? How much does this kind of coverage cost? Insurance Business answers these questions and more in this guide.
Auto insurance companies don’t actually offer a product called full coverage car insurance. What sounds like a policy that covers you and your vehicle from every possible risk is really a combination of state-mandated policies, plus collision and comprehensive coverage.
Therefore, what comprises full coverage insurance varies depending on where you live. And based on your personal circumstances, you may also be required to take out additional coverages or endorsements to be considered fully covered.
Generally, full coverage car insurance consists of three types of policies. These are liability car coverage – being a requirement in almost all states – as well as collision and comprehensive car insurance. Let’s go over each of these coverages.
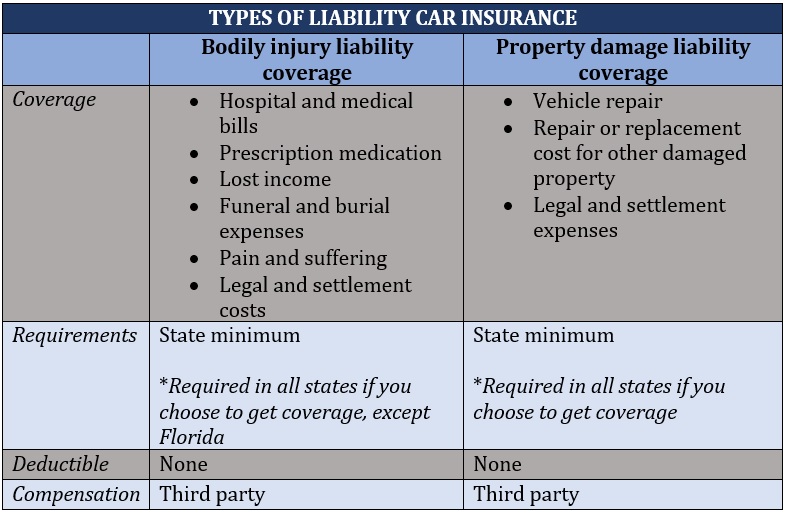
As the name suggests, liability car insurance covers you if you’ve been found legally responsible for an accident that results in another person’s injury, property damage, or death. It is often considered the foundation of a car insurance policy as almost all states require drivers to carry this form of coverage.
Liability car insurance comes in two parts. These are:
Under liability car coverage, your insurance carrier pays the entire cost of the liability claim, subject to the policy’s coverage limits. That’s why it doesn’t come with a deductible. The person who has filed the claim against you receives compensation.
The table below sums up the key elements of these two types of auto liability policies.
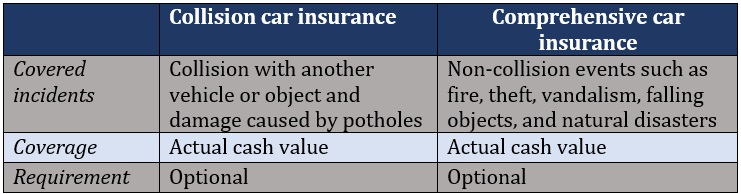
Collision coverage pays for the cost of repairing or replacing your car if it collides with another vehicle or object, or if it rolls over. This type of policy also covers damage caused by potholes. Collision car insurance doesn’t cover mechanical breakdown and normal wear and tear.
This type of policy works if you cause an accident. If the other driver is at fault, you can file a claim against their auto liability coverage.
Comprehensive car insurance complements collision coverage, that’s why they’re often bundled together. It covers the cost of repairing or replacing your vehicle if it is lost or damaged in a non-collision accident. These include man-made incidents such as arson, theft, and vandalism, and natural calamities like hailstorms and hurricanes. Comprehensive policies also cover damage caused by falling objects and animals.
Comprehensive coverage is sometimes confused with full coverage car insurance because of the terms used. You can learn more about this type of policy in our guide to comprehensive car insurance.
Both collision and comprehensive policies pay for the actual cash value of your vehicle. This means the value of your car at the time of purchase, minus depreciation. This is unless you have added a new car replacement endorsement to your auto policy.
In addition, both policies are optional if you’re the owner of the vehicle. Car dealerships, banks, and other lenders, however, will often require you to carry these types of coverages if you’re leasing a vehicle or taking out a car loan.
The table below sums up the key similarities and differences between collision and comprehensive car insurance.
Some states require additional coverages for a driver to have full coverage car insurance. These include:
This covers the cost of medical treatment you and your passengers incur because of an accident, regardless of who caused it. It also pays for your lost income and the cost of household services if your injury prevents you from doing such tasks. In addition, personal injury protection coverage pays out a death benefit, which can be used to cover funeral and burial costs.
This works the same way as PIP coverage but doesn’t cover lost income. MedPay can serve as your primary medical insurance after an accident or as supplemental coverage for your health insurance. As primary coverage, it pays for your immediate hospital and treatment expenses, while your health policy covers the rest. If used as supplemental cover, your health insurance covers your medical bills while MedPay reimburses the deductibles and co-pays.
Often packaged together, UM and UIM policies are designed to fill the gap between the costs you incur in a vehicular accident and the at-fault driver’s ability to pay. UM coverage compensates you and your passengers for the injuries and property damage you sustain if you’re hit by an uninsured driver. UIM coverage, meanwhile, pays out if the at-fault driver’s auto policy isn’t enough to cover the entire costs.
Apart from these coverages, there are a wide range of auto policies that you can choose from to further enhance your car coverage. You can learn more about these policies in our guide to car insurance types in the US.
Despite the name, full coverage car insurance doesn’t provide protection in every possible situation. Here are some scenarios that a full coverage auto policy doesn’t typically cover:
You can gain a deeper understanding of how car insurance works by checking out this comprehensive guide.
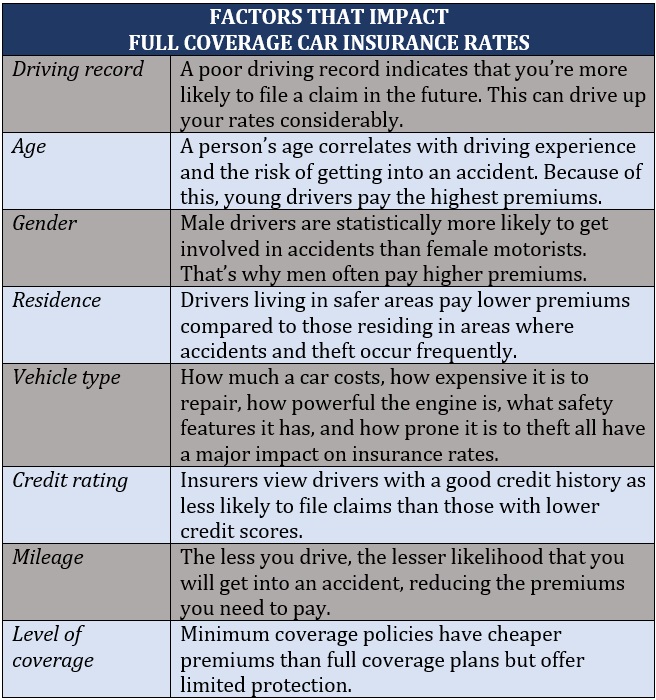
Because auto insurance is a highly individualized form of coverage, it is difficult to get a one-size-fits-all estimate of how much full coverage car insurance costs. But based on the various price comparison and insurer websites that Insurance Business checked out, full coverage policies cost more than twice as much as minimum coverage plans. This estimate is for policies combining liability, collision, and comprehensive car coverage.
For policies that include other state-mandated policies, the price difference can be higher. The type of coverage, however, isn’t the only factor that affects the premiums for your full coverage car insurance. The table below lists some of the other factors that play a huge role in determining insurance rates.
Full coverage car insurance can be expensive, but there are steps you can take to slash your premiums. You can find practical tips on how you can access cheap car insurance in this guide.
Full coverage car insurance isn’t compulsory but there are certain scenarios that will require you to take out this type of coverage.
If your vehicle is under financing, your bank will typically require you to be fully covered as a condition for your car loan. This means that you must have at least minimum liability coverage, as well as collision and comprehensive car insurance.
These same requirements are often imposed if you’re leasing a vehicle. You can learn more about how insurance for leased cars works in this guide.
The reason why car dealerships, lenders, and rental car companies require full coverage is to ensure that they are financially protected if the car is damaged or lost before the loan is paid off or your lease ends.
If you own a high-value car, getting full coverage car insurance is a good idea, even if the vehicle is fully paid for. This way you can also access new car replacement coverage, which pays the cost of replacing your vehicle with the same make and model if it gets totaled.
However, if the cost of full coverage insurance is higher than your car’s value, it’s better to skip this kind of coverage. Some experts also suggest dropping coverage if your vehicle’s value is four to six times less than the annual cost of collision and comprehensive car insurance combined. This is the point where it’s better to pay for the repairs yourself.
When working out how to get the most out of your auto insurance, it’s always best to assess what kind of protection you need. This guide explains what you should look for in a car insurance policy to help you find the right coverage.
Do you think full coverage car insurance is a worthwhile investment? Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.
